Gallstones are a common medical condition that affects millions of people worldwide. These small, hardened deposits form in the gallbladder, a pear-shaped organ located beneath the liver, and can lead to a range of symptoms and complications. While many gallstones remain silent and cause no harm, others can lead to serious medical conditions if left untreated.
In this blog, we’ll delve into what gallstones are, why complications occur, how they manifest, and the treatment options available. Understanding these aspects is crucial for patients to make informed decisions about their health and seek timely intervention.

What Are Gallstones?
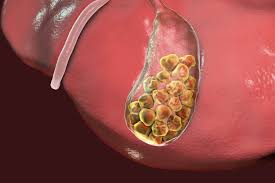
Gallstones are solid particles that develop in the gallbladder when substances in bile, such as cholesterol or bilirubin, become imbalanced. They vary in size, ranging from tiny grains of sand to larger stones resembling pebbles. Gallstones are categorized into two main types:
- Cholesterol Gallstones: The most common type, primarily composed of cholesterol.
- Pigment Gallstones: Made of bilirubin, these are less common and are more likely to occur in people with certain medical conditions, such as liver disease or infections in the bile ducts.
While gallstones can be asymptomatic (silent gallstones), they may also lead to complications if they obstruct bile flow.
Why Do Gallstones Become Complicated?
Complications arise when gallstones move out of the gallbladder and block the flow of bile in the bile ducts or other associated pathways. This blockage can trigger inflammation, infection, or even severe damage to surrounding organs.
Factors that increase the risk of complications include:
- Size of the Gallstones: Larger stones are more likely to obstruct ducts.
- Location: Stones that migrate into the bile ducts are more problematic.
- Underlying Conditions: People with diabetes or weakened immune systems are at higher risk.
- Delay in Treatment: Ignoring symptoms or delaying medical care can lead to severe outcomes.

Common Complications of Gallstones
1. Cholecystitis (Inflammation of the Gallbladder)
This occurs when gallstones block the cystic duct, leading to inflammation and infection. Symptoms include:
- Severe pain in the upper right abdomen
- Fever
- Nausea and vomiting
If untreated, cholecystitis can lead to perforation (rupture) of the gallbladder, a life-threatening condition.
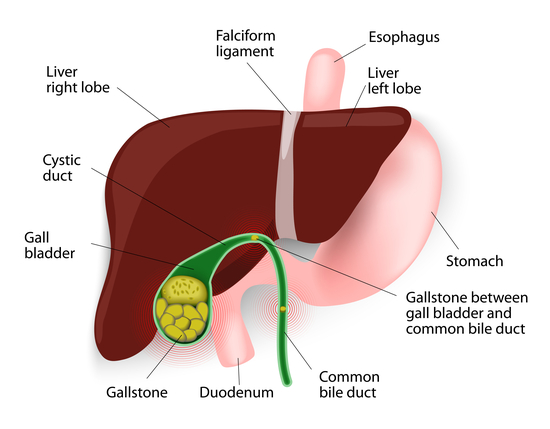
2. Choledocholithiasis (Bile Duct Stones)
When gallstones travel to the bile ducts, they obstruct bile flow, leading to:
- Jaundice (yellowing of the skin and eyes)
- Dark urine and pale stools
- Persistent pain in the upper abdomen
Choledocholithiasis can also cause bile duct infections (cholangitis), which require immediate medical attention.
3. Pancreatitis (Inflammation of the Pancreas)
If a gallstone blocks the pancreatic duct, it can lead to pancreatitis, characterized by:
- Intense abdominal pain radiating to the back
- Fever
- Nausea and vomiting
Severe pancreatitis can result in complications like organ failure or chronic inflammation.
4. Gallstone Ileus
A rare but serious complication where a large gallstone enters the intestinal tract, causing an obstruction. Symptoms include:
- Severe abdominal bloating
- Constipation or inability to pass gas
- Vomiting
This condition typically requires surgical intervention.
5. Gallbladder Cancer
While rare, chronic inflammation caused by gallstones is a risk factor for gallbladder cancer. Early detection and regular monitoring are critical for individuals with persistent gallstone issues.
Signs and Symptoms of Gallstone Complications
Recognizing the symptoms of complicated gallstones is crucial for seeking timely treatment. Common signs include:
- Persistent pain in the upper right abdomen, especially after meals
- Fever and chills
- Jaundice
- Nausea and vomiting
- Abdominal tenderness
If you experience any of these symptoms, especially in combination, consult a healthcare provider immediately.

Diagnosing Gallstone Complications
Accurate diagnosis involves a combination of medical history, physical examination, and diagnostic tests. Key procedures include:
- Ultrasound: The most common imaging test to detect gallstones and inflammation.
- CT Scan or MRI: Used to evaluate complications like pancreatitis or bile duct obstructions.
- Endoscopic Retrograde Cholangiopancreatography (ERCP): A specialized procedure to locate and remove bile duct stones.
- Blood Tests: To check for infection, liver function, and inflammation markers.
Treatment Options for Gallstone Complications
Treatment depends on the severity of the condition, the location of the stones, and the patient’s overall health. Options include:
1. Medications
- Pain relievers and antibiotics for infection control.
- Oral bile acids to dissolve small cholesterol stones (effective only in select cases).
2. Endoscopic Procedures
- ERCP: Both diagnostic and therapeutic, this procedure removes stones from the bile ducts.
3. Surgical Intervention
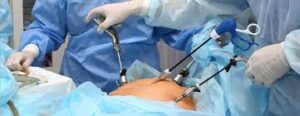
- Cholecystectomy (Gallbladder Removal):
- Laparoscopic Cholecystectomy: Minimally invasive and the most common approach for gallstone complications.
- Open Cholecystectomy: Performed in cases of severe inflammation or complications.
4. Drainage Procedures
In cases of abscess or perforation, a drainage procedure may be required before or during surgery.
Recovery and Lifestyle Adjustments
Post-Surgery Recovery
- Laparoscopic surgery typically involves a shorter recovery period (1–2 weeks).
- Open surgery may require longer recovery (4–6 weeks).
Lifestyle Changes
To prevent future issues and support overall health:
- Dietary Adjustments: Adopt a low-fat diet, as high-fat meals can trigger symptoms.
- Maintain a Healthy Weight: Obesity is a significant risk factor for gallstones.
- Regular Exercise: Helps in weight management and improves digestion.
- Stay Hydrated: Proper hydration supports bile production and reduces stone formation.
FAQs
1. Can gallstones go away on their own?
Silent gallstones may not require treatment, but symptomatic or complicated gallstones usually need medical intervention.
2. Is gallbladder removal safe?
Yes, cholecystectomy is a routine procedure with a high success rate. The body adapts well to the absence of the gallbladder.
3. Can gallstones recur after treatment?
Gallstones cannot recur after gallbladder removal. However, bile duct stones can form in rare cases.
4. What are the risks of untreated gallstone complications?
Untreated complications can lead to severe infections, organ damage, or even death in rare cases. Prompt treatment is essential.
5. Can diet alone prevent gallstones?
A healthy diet helps reduce risk factors but cannot guarantee prevention, especially if genetic predisposition exists.
Why Choose Dr. Pallab Saha for Gallstone Treatment?
Dr. Pallab Saha, a renowned general and laparoscopic surgeon in Kolkata, specializes in the treatment of gallstones and their complications. With 18 years of experience and expertise in advanced surgical techniques, he ensures precise diagnosis, effective treatment, and personalized care for each patient.
At R G Stone Urology and Laparoscopy Hospital, Dr. Saha employs cutting-edge technology to deliver minimally invasive solutions, ensuring quicker recovery and optimal outcomes.
Final Thoughts
Complications from gallstones can significantly impact your quality of life, but timely diagnosis and expert care can prevent serious outcomes. Whether you are dealing with gallstones for the first time or have experienced recurrent issues, understanding the risks and treatment options is vital.
If you’re experiencing symptoms or seeking expert advice, schedule a consultation with Dr. Pallab Saha today. Your journey to better health begins with the right care.