Gallbladder stones, or cholelithiasis, affect millions of people worldwide, often leading to discomfort and severe complications if left untreated. While most individuals recognize gallstones as solid particles formed within the gallbladder, fewer people understand the critical role that chronic inflammation plays in their development and formation. Chronic inflammation, a prolonged immune response, can significantly contribute to gallstone formation, exacerbating the symptoms and complications associated with gallbladder diseases.
This blog will explore the intricate relationship between chronic inflammation and gallbladder stone formation, providing insights into causes, symptoms, treatments, and preventive strategies for managing this common yet potentially dangerous condition.

Understanding Gallbladder Stones
What Are Gallbladder Stones?
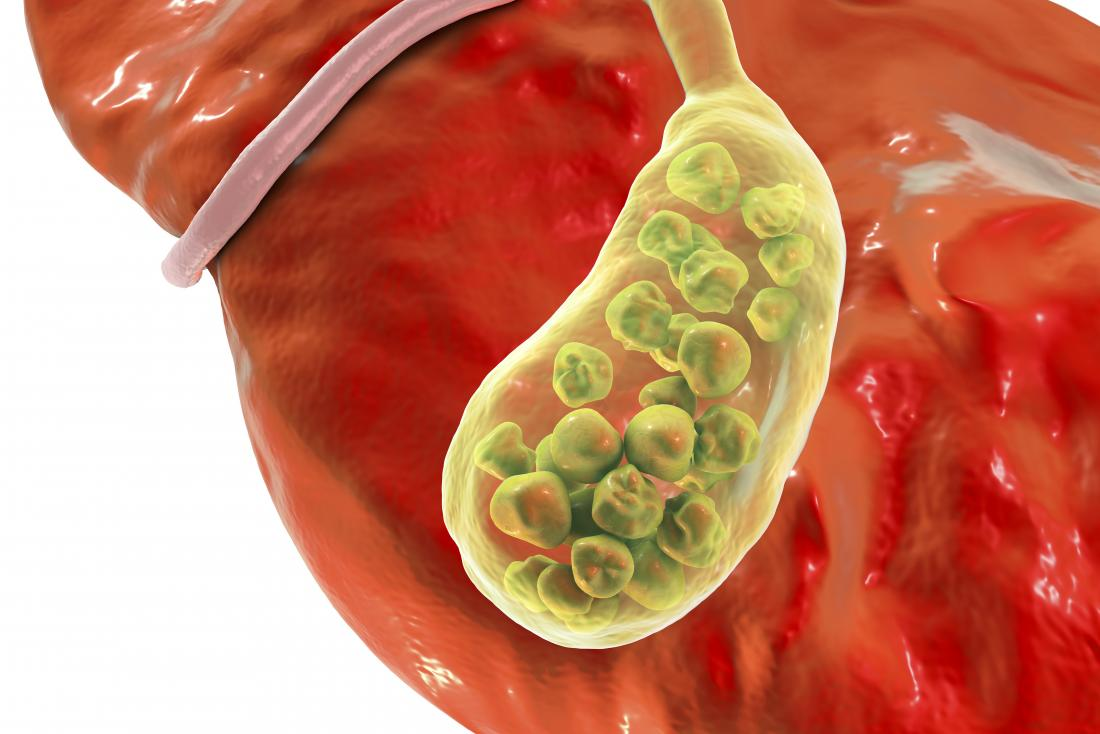
Gallbladder stones, or gallstones, are hardened deposits of digestive fluid that form in the gallbladder, a small organ located beneath the liver. The gallbladder’s primary function is to store bile, a fluid produced by the liver that helps digest fats. Gallstones can vary in size from as small as a grain of sand to as large as a golf ball, and they come in two main types:
- Cholesterol Gallstones: The most common type, composed primarily of undissolved cholesterol.
- Pigment Gallstones: Dark stones made from excess bilirubin, a chemical produced during the breakdown of red blood cells.
Symptoms of Gallbladder Stones
Gallstones can be asymptomatic in many cases, meaning that individuals may not experience any discomfort. However, when gallstones block the bile ducts, they can trigger intense pain known as a gallbladder attack or biliary colic. Symptoms may include:
- Sudden, severe pain in the upper right abdomen or center of the abdomen
- Pain that radiates to the right shoulder or back
- Nausea and vomiting
- Fever and chills (in cases of infection)
- Jaundice (yellowing of the skin and eyes due to bile obstruction)

Complications of Gallstones
If gallstones block the bile ducts, it can lead to severe conditions such as:
- Cholecystitis: Inflammation of the gallbladder, often resulting in infection.
- Pancreatitis: Inflammation of the pancreas caused by blockage of the pancreatic duct.
- Choledocholithiasis: Gallstones lodged in the common bile duct, causing jaundice and liver damage.
The Role of Chronic Inflammation in Gallstone Formation
Chronic Inflammation: What Is It?
Inflammation is the body’s natural defense mechanism against injury, infection, and disease. While acute inflammation is a short-term response to trauma, chronic inflammation is a prolonged, low-grade immune response that can persist for months or even years. This persistent inflammation is associated with various chronic diseases, including gallbladder conditions and gallstone formation.
How Does Chronic Inflammation Contribute to Gallstone Formation?
- Bile Imbalance: Chronic inflammation of the gallbladder, known as chronic cholecystitis, can lead to changes in bile composition. Normally, bile consists of bile salts, cholesterol, and bilirubin, which work together to digest fats. Inflammation can disrupt this balance, causing the cholesterol in bile to crystallize and form stones.
- Gallbladder Dysfunction: Chronic inflammation can damage the gallbladder’s ability to contract and release bile efficiently. When bile becomes stagnant, it increases the likelihood of stone formation. The reduced motility, also known as gallbladder dyskinesia, leads to bile stasis, which is a primary contributor to stone development.
- Mucus Hypersecretion: Chronic inflammation triggers excessive mucus production in the gallbladder lining. This mucus can trap cholesterol crystals, encouraging them to grow into larger stones over time. The thickened bile becomes more viscous, which further promotes gallstone formation.
- Scarring and Fibrosis: Prolonged inflammation can result in scarring or fibrosis of the gallbladder walls. This stiffening and thickening of the gallbladder wall reduce its functionality, contributing to bile stasis and further encouraging the formation of stones.
- Oxidative Stress and Cellular Damage: Chronic inflammation often involves the release of free radicals and oxidative stress, which damage the cells of the gallbladder lining. This damage can initiate a cascade of immune responses that ultimately lead to gallstone formation.

Chronic Inflammatory Conditions Linked to Gallstone Formation
Several chronic conditions are linked to increased inflammation, which may predispose individuals to gallstone formation:
- Obesity: Excess body weight leads to chronic low-grade inflammation and increases cholesterol levels in bile, making gallstones more likely.
- Diabetes: People with diabetes often have higher levels of triglycerides, a type of fat that contributes to gallstone formation, and are more prone to chronic inflammation.
- Liver Disease: Conditions like cirrhosis, which involve chronic inflammation of the liver, can alter bile production and increase the risk of pigment gallstones.
- Crohn’s Disease: Individuals with inflammatory bowel diseases, such as Crohn’s, experience chronic inflammation in the digestive tract, which can influence bile composition and gallstone risk.
Prevention and Management of Gallstones Related to Chronic Inflammation
Lifestyle Modifications
To prevent gallstone formation, especially in individuals prone to chronic inflammation, certain lifestyle changes can help:
- Maintain a Healthy Weight: Avoid rapid weight loss or weight gain, as these can disturb bile production and increase cholesterol levels.
- Eat a Balanced Diet: Focus on a high-fiber diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains while limiting refined sugars and unhealthy fats. This helps in reducing inflammation and cholesterol levels.
- Exercise Regularly: Physical activity can help manage body weight and reduce inflammation in the body.
- Stay Hydrated: Drinking plenty of water ensures proper bile flow and reduces the risk of bile stasis.
Medical Treatment for Chronic Inflammation and Gallstones
For individuals with chronic inflammation leading to gallstone formation, medical intervention may be required:
- Anti-inflammatory Medications: Doctors may prescribe anti-inflammatory drugs to manage chronic inflammation, which can reduce the risk of gallstone formation.
- Cholecystectomy: In cases where gallstones cause significant pain or complications, surgical removal of the gallbladder (cholecystectomy) may be necessary. This is a common and effective treatment to prevent future gallstone-related issues.
- Bile Acid Therapy: Medications like ursodeoxycholic acid can help dissolve cholesterol gallstones and reduce inflammation, though this approach is usually used in patients who cannot undergo surgery.
Conclusion
The relationship between gallbladder stones and chronic inflammation is multifaceted, with inflammation playing a significant role in stone formation. Chronic conditions such as obesity, diabetes, and inflammatory diseases further increase the risk of developing gallstones. Understanding the impact of chronic inflammation on gallbladder function and bile composition is crucial for both prevention and treatment.
By addressing the underlying causes of chronic inflammation and adopting healthy lifestyle habits, individuals can significantly reduce their risk of gallstone formation. Additionally, medical and surgical treatments offer effective ways to manage and treat gallbladder stones, providing relief from pain and preventing severe complications.
If you experience symptoms of gallstones or suspect chronic inflammation, seeking medical advice early can prevent further complications and ensure appropriate treatment. Managing inflammation and gallstone risk through proactive healthcare measures is key to maintaining both gallbladder and overall health.