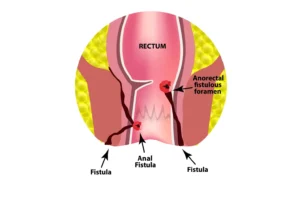
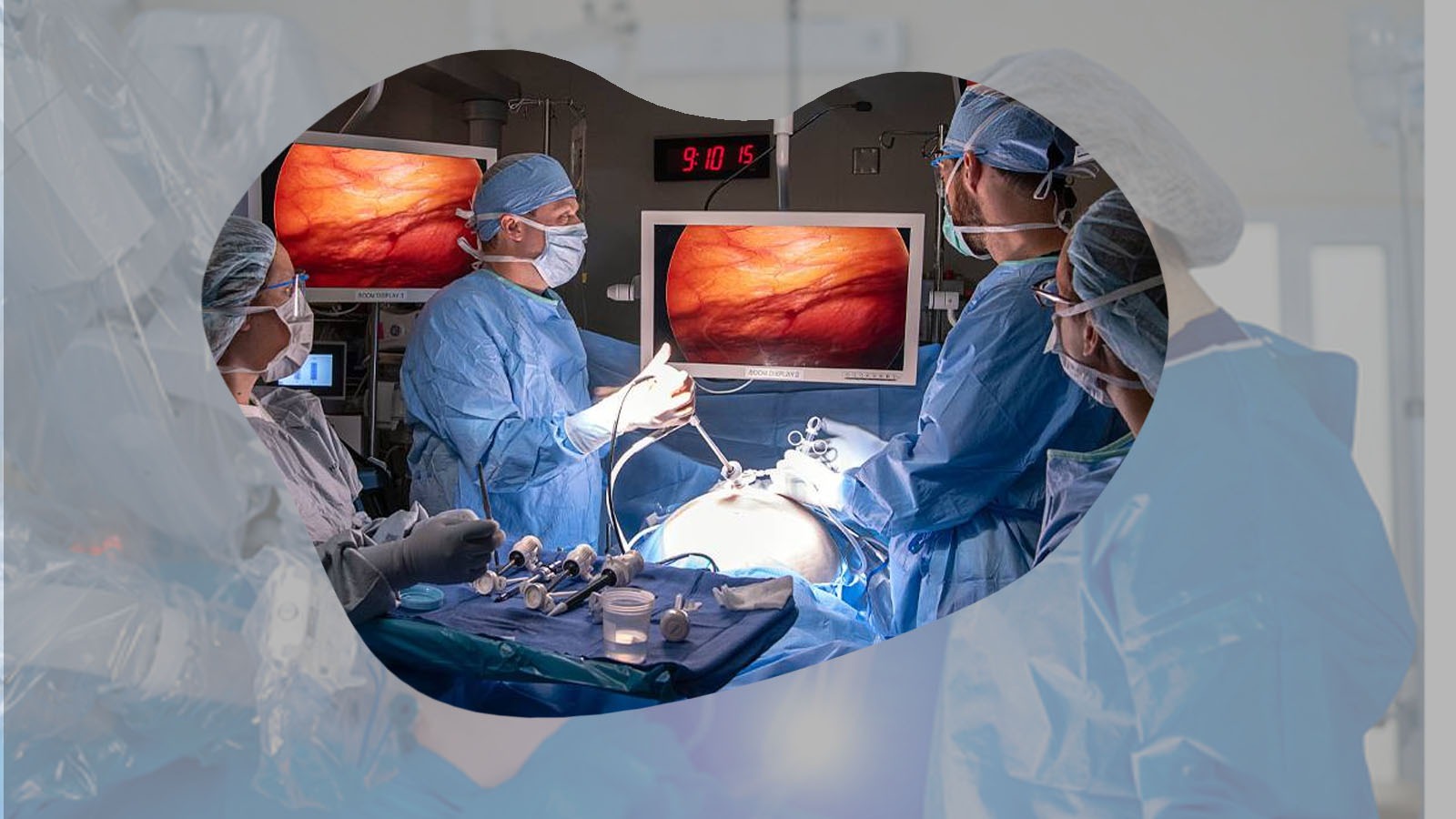
Introduction
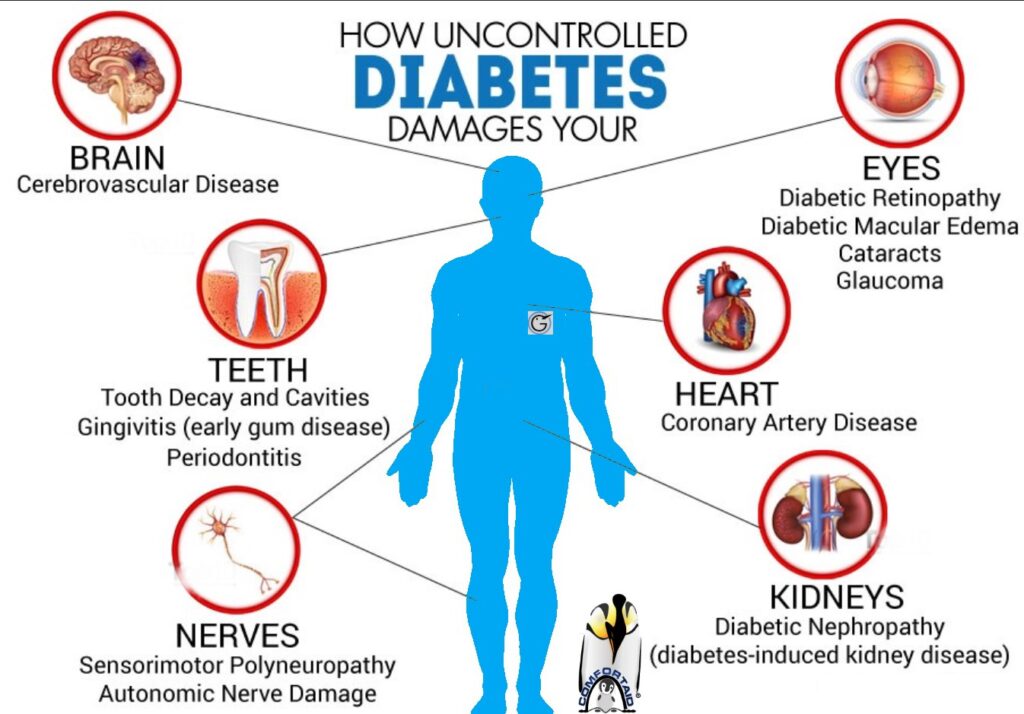
Diabetic gangrene is a severe complication of diabetes, often resulting from poorly controlled blood sugar levels leading to vascular damage, neuropathy, and a compromised immune response. This condition requires a comprehensive, multidisciplinary approach to ensure optimal patient outcomes and prevent life-altering consequences, such as amputation. Here, we explore the critical aspects of managing diabetic gangrene through collaborative care.

1. Early Diagnosis and Risk Assessment
The foundation of effective management lies in early diagnosis. Identifying diabetic gangrene at its initial stages can significantly reduce complications.
- Endocrinologists play a vital role in optimizing blood sugar control to prevent further vascular damage and enhance wound healing.
- Vascular surgeons assess blood flow to the affected area using advanced imaging techniques like Doppler ultrasound or angiography, determining the severity of ischemia.
- Podiatrists focus on regular foot examinations to detect early signs of ulcers, infections, or necrosis, especially in high-risk patients.
2. Medical Management
A tailored medical plan is essential for controlling infection, improving circulation, and supporting overall health.
- Infectious disease specialists prescribe broad-spectrum antibiotics initially, switching to targeted therapy based on culture and sensitivity results. This helps combat polymicrobial infections often associated with diabetic gangrene.
- Endocrinologists fine-tune insulin therapy or oral hypoglycemics to maintain blood glucose levels within a narrow range, crucial for tissue repair.
- Pain management specialists provide relief through pharmacological and non-pharmacological means, addressing the physical and psychological toll of chronic pain.
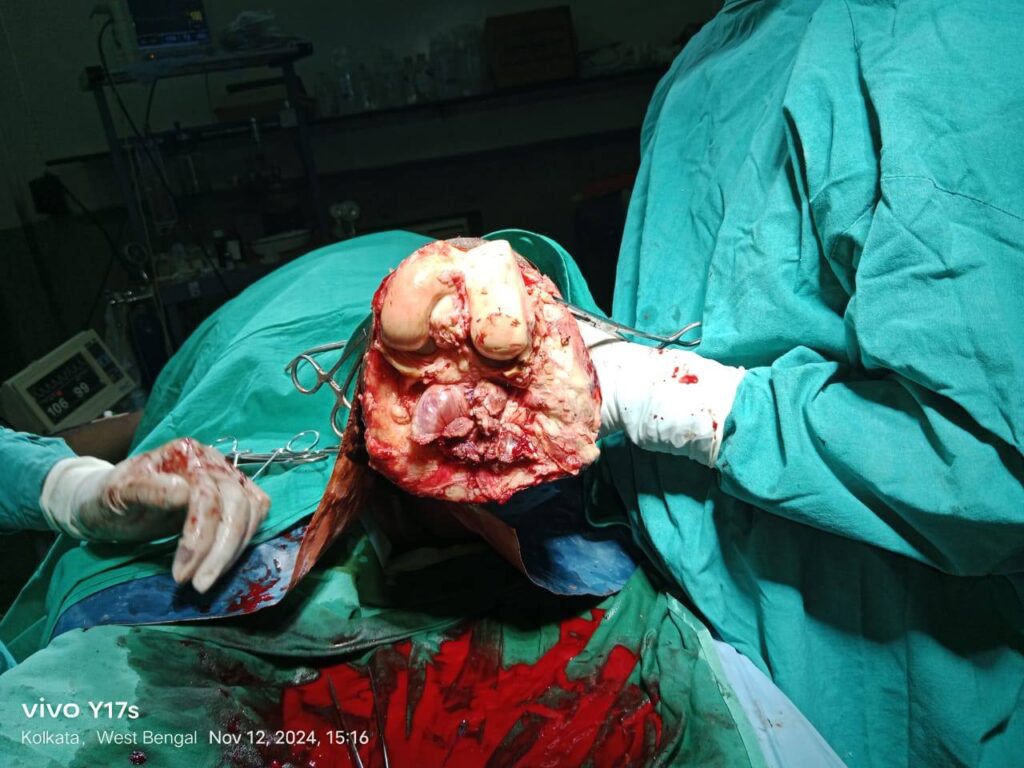
3. Surgical Interventions
When conservative treatments are insufficient, surgical procedures become necessary.
- Debridement: Surgeons remove necrotic tissue to prevent the spread of infection and promote healing.
- Revascularization: Vascular surgeons perform procedures like angioplasty, stenting, or bypass surgery to restore blood flow to ischemic areas.
- Amputation: In extreme cases, where gangrene has progressed extensively, surgeons may perform amputations to save the patient’s life. This decision is made collaboratively, considering the patient’s overall health and quality of life.
4. Wound Care and Rehabilitation
Comprehensive wound care is pivotal in managing diabetic gangrene.
- Wound care specialists employ advanced dressings, negative pressure wound therapy, and hyperbaric oxygen therapy to accelerate healing.
- Physical therapists assist patients with mobility issues, designing exercises to improve circulation and strength post-surgery or amputation.
- Occupational therapists help patients adapt to lifestyle changes, including the use of prosthetics or mobility aids, ensuring independence and functionality.
5. Psychological Support
The psychological impact of diabetic gangrene and its treatments can be profound.
- Psychologists provide counseling to address feelings of anxiety, depression, or grief, particularly for patients facing amputation or significant lifestyle changes.
- Support groups offer community and shared experiences, helping patients cope with the challenges of recovery.
6. Preventive Measures
Prevention remains the cornerstone of managing diabetic complications.
- Patient education: Patients are taught proper foot care, the importance of glycemic control, and recognizing early signs of infection or ischemia.
- Regular check-ups: Multidisciplinary clinics ensure patients receive consistent monitoring and preventive interventions, reducing the likelihood of recurrent gangrene.
- Lifestyle modifications: Dietitians and diabetes educators work with patients to adopt a healthy lifestyle, emphasizing balanced nutrition, physical activity, and smoking cessation.

The Power of Collaboration
Diabetic gangrene is a complex condition that demands the expertise of multiple medical disciplines. A collaborative approach not only improves patient outcomes but also enhances the quality of life by addressing the condition holistically. By combining timely interventions, advanced medical therapies, and compassionate care, healthcare providers can mitigate the devastating impact of diabetic gangrene.
For patients and healthcare teams alike, the message is clear: managing diabetic gangrene is not just about treating a condition—it’s about restoring hope and preserving life. Contact Us Now