Gall stones are hardened deposits that form within the gall bladder, a small organ located beneath the liver. These stones can range in size from tiny grains to structures as large as golf balls. Although gallstones are common and often asymptomatic, their potential link to gallbladder cancer is a subject of significant concern. Understanding this connection is crucial for early detection and prevention strategies.
Gallstones: The Silent Culprit
Gallstones are primarily composed of cholesterol or bilirubin, substances naturally present in bile. They often go unnoticed but can cause severe pain and complications when they obstruct the bile ducts, leading to conditions like cholecystitis (inflammation of the gallbladder) or pancreatitis.
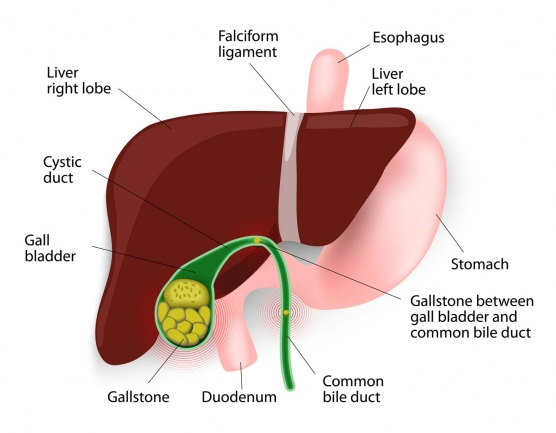
Gallbladder Cancer: A Hidden Threat
Gallbladder cancer, though rare, is particularly dangerous due to its tendency to be diagnosed at advanced stages. Most cases are adenocarcinomas, cancers that originate in the glandular cells lining the gallbladder. The disease often remains undetected until it has spread, resulting in a poor prognosis and limited treatment options.
Unveiling the Connection: Gallstones and Gallbladder Cancer
Research has demonstrated a significant correlation between gallstones and the development of gallbladder cancer. Chronic inflammation and irritation caused by gallstones are believed to contribute to the malignant transformation of gallbladder cells over time. However, it’s important to note that while gallstones increase the risk, they do not guarantee cancer development.
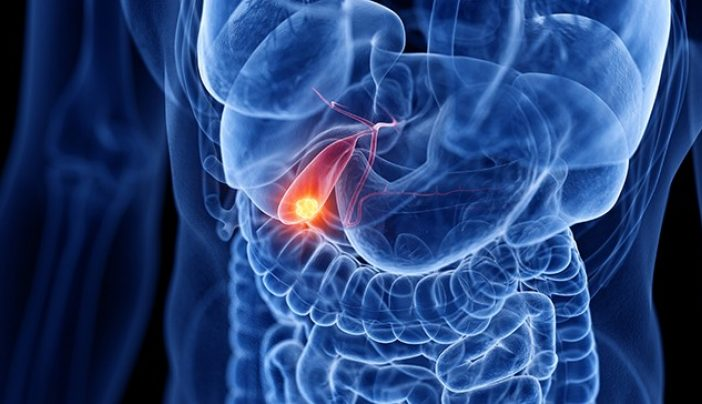
Preventive Measures: Mitigating the Risks
Reducing the risk of gallstone formation is a key strategy in lowering the potential for gallbladder cancer. Lifestyle modifications, such as maintaining a healthy weight and a diet rich in fiber, can help prevent gallstones. Additionally, avoiding rapid weight loss and excessive high-fat foods is beneficial.
Vigilance and Awareness: Early Detection
Regular medical check-ups and imaging studies are vital for the early detection of both gallstones and gallbladder cancer. Recognizing symptoms like abdominal pain, jaundice, and unexplained weight loss can lead to timely intervention and better outcomes.

Navigating Treatment Options
For those with gallstones, treatment typically involves a cholecystectomy, the surgical removal of the gallbladder, which also eliminates the risk of gallbladder cancer. If gallbladder cancer is diagnosed, treatment options may include surgery, chemotherapy, and radiation therapy, depending on the stage of the disease.
Empowering Through Knowledge
Raising awareness about the link between gallstones and gallbladder cancer is crucial. By educating individuals on risk factors, symptoms, and preventive measures, we empower them to take proactive steps toward their health and seek timely medical attention when needed.
Deep Dive into Gallstones and Their Complications
1. Causes of Gallstones Gallstones form due to an imbalance in the substances that make up bile, such as cholesterol and bilirubin. Factors contributing to this imbalance include a high-fat diet, obesity, rapid weight loss, and certain medical conditions like diabetes.
2. Symptoms of Gallstones While many people with gallstones remain asymptomatic, symptoms can occur when stones block the bile ducts. This blockage causes severe abdominal pain, particularly in the upper right abdomen, often accompanied by nausea and vomiting.
3. Diagnosis and Treatment of Gallstones Gallstones are diagnosed through imaging tests such as ultrasounds or CT scans. Depending on the severity, treatment options include medications to dissolve the stones or surgical removal of the gallbladder (cholecystectomy).
4. What is Gallbladder Cancer? Gallbladder cancer starts in the cells lining the gallbladder. It is a rare but aggressive cancer that can spread to nearby organs if not detected early. Symptoms often mimic those of less serious conditions, leading to delays in diagnosis.
5. Risk Factors for Gallbladder Cancer Risk factors include a history of gallstones, chronic inflammation of the gallbladder, obesity, certain genetic conditions, and age (most common in people over 65).
6. The Relationship Between Gallstones and Gallbladder Cancer Chronic irritation and inflammation from gallstones are believed to play a role in the development of gallbladder cancer. This relationship highlights the importance of managing gallstones proactively.
7. Complications of Gallstones Beyond the risk of cancer, gallstones can lead to severe complications such as acute cholecystitis, bile duct obstruction, and pancreatitis, each requiring prompt medical intervention.
8. Prevention of Gallstones Preventing gallstones involves adopting a balanced diet, regular exercise, and maintaining a healthy weight. It’s also advisable to avoid rapid weight loss and reduce the intake of high-fat foods.

Conclusion: Bridging the Divide Between Gallstones and Gallbladder Cancer
Understanding the connection between gallstones and gallbladder cancer emphasizes the need for proactive health measures. By staying informed and making conscious lifestyle choices, individuals can reduce their risk and promote overall gallbladder health. Regular check-ups and early detection remain key in navigating and mitigating the risks associated with these conditions.
FAQs: Clarifying Common Concerns
1. Can gallstones lead to gallbladder cancer? Yes, although not everyone with gallstones develops cancer, the presence of gallstones increases the risk of gallbladder cancer due to chronic inflammation and irritation.
2. What are the warning signs of gallbladder cancer? Warning signs include persistent abdominal pain, jaundice (yellowing of the skin and eyes), unexplained weight loss, and nausea.
3. How is gallbladder cancer diagnosed? Diagnosis typically involves imaging tests like ultrasound, CT scans, and MRI, followed by a biopsy to confirm the presence of cancerous cells.
4. What are the treatment options for gallbladder cancer? Treatment may include surgical removal of the gallbladder, chemotherapy, and radiation therapy, depending on the stage and extent of the cancer.
5. Can gallbladder cancer be prevented? While it can’t always be prevented, maintaining a healthy lifestyle and addressing risk factors like obesity and gallstone formation can reduce the risk. Regular medical check-ups are also crucial for early detection.
By bridging the gap between gallstones and gallbladder cancer through awareness and education, we can take steps toward reducing the burden of these conditions. Let’s strive for early detection, effective treatment, and proactive prevention to safeguard our health and well-being. Consulting with a healthcare professional, like Dr. Pallab Saha, can provide you with the appropriate evaluation and personalized treatment needed to address your condition.